Ovulation Induction

Regular ovulation is associated with regular menstruation. If you have irregular periods, occasional periods or no periods it may mean you have an ovulation condition. If you have an ovulation condition and are trying to conceive it may require medication to induce normal follicle development and regular ovulation.
If you have regular menstrual cycles, e.g. in unexplained or poorly explained fertility, your fertility specialist may recommend ovulation induction medication in an attempt to increase the chance of pregnancy.
Enquire Today
How does ovulation induction work?
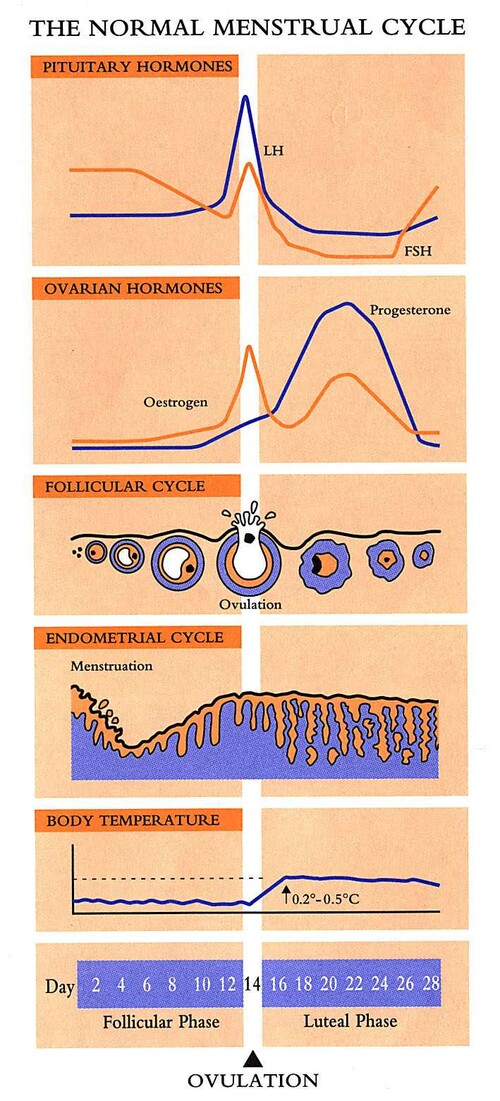
Ovulation can be confirmed after the event by a blood test to measure progesterone. Your fertility specialist can be alerted to imminent ovulation by:
- Urinary LH testing (ovulation detection kit): Many women will already be using urinary ovulation detection kits. These kits detect the pre-ovulatory LH surge that occurs approximately 24 hours before ovulation. The best time for intercourse is 24 to 36 hours after the LH surge.
- Ultrasound cycle tracking: The development of the ‘leading follicle’ - the follicle which contains the egg which is likely to ovulate in a particular cycle - can be tracked by ultrasound scan. Your fertility specialist will arrange to commence tracking four to five days prior to anticipated ovulation. If a woman is having hormone treatment for fertility assistance there may be several suitable follicles developing at the same
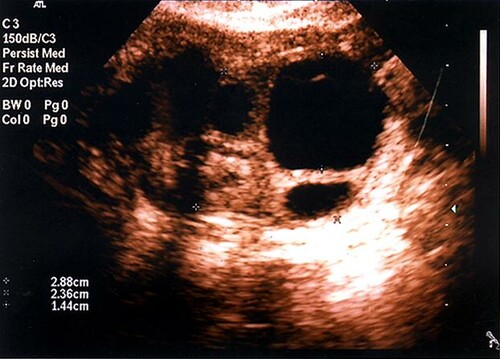
Am I suitable for ovulation induction?
There are many possible reasons why women may not ovulate regularly. Some women have a signalling problem between the brain and the ovaries which means that the normal hormone pathways do not operate effectively. This results in irregular, rare or absent ovulation. This is common in women who exercise at a very high level and in women who are underweight. It is also common in women who engage in shift work, for example flight attendants.
Some women have polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), a very common hormonal condition associated with long cycles or infrequent or absent periods, excess activity of some hormones and which is sometimes associated with weight gain, excess facial and body hair, acne and insulin resistance.
Various other hormonal imbalances may also cause irregular ovulation, such as abnormalities of prolactin secretion or of thyroid function.
Another serious cause of ovulation failure is premature menopause. This may be temporary or permanent. When the ovaries have exhausted their supply of eggs, this usually results in premature menopause. This condition will not respond to ovulation induction medication and your fertility specialist may discuss the use of donor eggs.
Very occasionally there may be a significant problem within the ovaries with the development of premature ovarian failure and damage to the little eggs and follicles. This can be temporary or permanent and is the only sort of ovulation problem which is not helped by the use of ovulation induction medications.Treatments
Clomiphene citrate
The most commonly used medicine is an oral preparation called clomiphene citrate (sold as Clomid® or Serophene®). Clomiphene works by blocking oestrogen receptors, thereby tricking the brain into increased follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) production. This will normally result in the development of one or more mature follicles and consequent ovulation. A common side effect of Clomiphene therapy is temporary hot flushes due to blocking of the oestrogen receptors.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Another medication commonly used is FSH injections. These work directly on the ovaries to develop a follicle(s). Both these medications, especially FSH injections, may cause multiple follicle development, with the risk of multiple pregnancy. For this reason your fertility specialist will perform regular ultrasounds to determine the number and rate of growth of these follicles. If more than one follicle develops, your fertility specialist will discuss the risks of multifollicular ovulation.
Rarely, an additional medication called luteinising hormone (LH) is used to aid follicle development. Your fertility specialist will advise if this is required. After the follicle has developed your fertility specialist may use another injection of synthetic human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to trigger the release of the egg from the follicle. The fertile time is for 36 hours from the time of trigger.
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Clomiphene or FSH may be used in conjunction with timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination (IUI) which ensures that the sperm is introduced into the uterus at the right time. Read more about IUI
Next steps
To find out more about how to regulate your cycle or the simple treatment of ovulation induction and the costs involved please call 1800 111 483 or fill in the form below.
Understanding your ovulation calendar
Learn more about female fertility tests